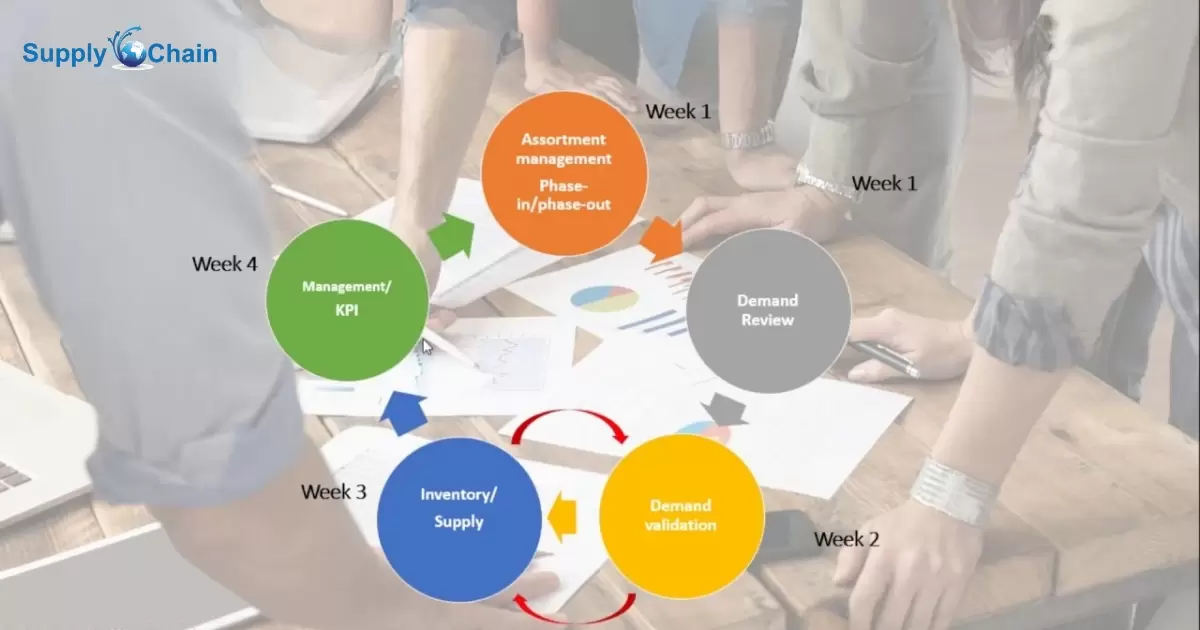
Supply chain management involves five basic steps to ensure products move efficiently from production to consumers. First, plan what to produce, how much, and when. Next, source the necessary materials from suppliers. Once materials are on hand, make the product.
It’s all about the 5 basic steps of supply chain management. From planning what to produce to distributing the final product, it’s a simple yet crucial process. Let’s unravel the mystery behind What are the 5 basic steps of supply chain management?
The 5 basic steps of supply chain management serve as a crucial roadmap for getting things done, mitigating potential challenges such as Supply Chain Risks. It starts with planning – deciding what to produce and how much.
Importance Of Accurate Demand Forecasts
Demand forecasts are like a crystal ball for businesses. They help companies predict what customers want and when, preventing guesswork. With precise forecasts, businesses can optimize their inventory, ensuring they have enough products to meet demand without excess. This not only keeps customers happy but also saves money by avoiding overstocks or shortages.
Companies can allocate resources efficiently, plan production schedules effectively, and streamline their supply chains. This foresight not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances overall customer satisfaction. In the dynamic world of business, having a solid grasp on accurate demand forecasts is the key to staying ahead of the game.
Methods Of Demand Forecasting
There are several methods of demand forecasting, and businesses often use a combination of these approaches to enhance the accuracy of their predictions. Here are some common methods of demand forecasting:
Qualitative Methods
- Experts in the industry provide their opinions and insights based on their experience and knowledge.
- A group of experts independently assesses the situation, and their opinions are iteratively collected and summarized until a consensus is reached.
- Surveys, interviews, and focus groups are conducted to gather information from potential customers and industry participants.
Time Series Analysis
- Simple moving averages, or weighted moving averages, are used to smooth out fluctuations and identify trends in historical data.
- Assigns exponentially decreasing weights to past observations to give more weight to recent data.
- Examines historical data to identify long-term trends in demand.
Causal Models
- Examines the relationship between the dependent variable (demand) and one or more independent variables (factors influencing demand).
- Incorporates economic variables such as income, price levels, and consumer spending into the forecasting model.
It’s important for businesses to carefully select the appropriate method or combination of methods based on the nature of their industry, the availability of data, and the level of accuracy required for effective decision-making.
Inventory Planning
Inventory planning is like a puzzle where you need to find the right balance. First, you decide what to stock and how much, making sure not to overdo it or run out. It’s about predicting demand and keeping shelves stocked with just the right amount.
In the world of inventory planning, technology plays a crucial role. With the help of advanced systems, businesses can track stock levels, analyze sales patterns, and automate reordering. This not only saves time but also reduces the chances of errors.
| Key Aspects | Benefits |
| Accurate Forecasting | Minimizes Overstock and Understock Situations |
| Efficient Reordering | Reduces Holding Costs and Stockouts |
| Real-time Tracking | Enhances Supply Chain Visibility |
| Demand Analysis | Improves Customer Satisfaction |
| Risk Management | Mitigates Unforeseen Disruptions |
Determining Optimal Inventory Levels

Optimal inventory levels are like finding the sweet spot in a game of balancing. You want enough stock to meet customer demand without drowning in excess. The first step is understanding how fast products fly off the shelves. This helps in setting a baseline for what’s needed.
Once you’ve got that rhythm, it’s time to factor in lead times – how long it takes from ordering to arrival. This ensures you never run out during the crucial moments. Striking this delicate balance means smoother operations and happy customers. So, determining optimal inventory levels is not just a numbers game; it’s the art of keeping things just right.
Safety Stock Considerations
In the world of supply chain management, safety stock is like a safety net—it’s that extra stock kept on hand to guard against unexpected hiccups. Imagine you run a store, and suddenly there’s a surge in demand or a delay from suppliers. That’s where safety stock comes to the rescue, ensuring you have enough inventory to handle these surprises without leaving your shelves empty.
Determining the right amount of safety stock involves balancing the risk of shortages with the cost of carrying extra inventory. It’s a bit like deciding how many extra umbrellas to keep in your store—enough to weather the unexpected storm but not so many that they gather dust.
Route Optimization And Cost-Efficiency
In the world of logistics, route optimization is like finding the quickest path on a treasure map. It’s all about making sure trucks and delivery vehicles take the most efficient route possible, saving time and money.
Cost efficiency, in the context of route optimization, is about getting more bang for your buck. It’s like getting the best deal at the grocery store, but applied to moving goods. When routes are optimized, fuel is saved, fewer resources are used, and deliveries happen faster.
Warehousing And Distribution
Warehousing and distribution are crucial cogs in the business wheel. In simple terms, warehousing is like a safe home for products, where they wait until needed. Distribution, on the other hand, is the reliable messenger ensuring products reach their intended destinations – whether it’s a store shelf or directly to your doorstep.
Imagine a warehouse as a giant storage space, neatly organized to keep track of products. It’s like a waiting room where items chill until they get the green light to move. Distribution takes the stage when it’s time for the products to leave this waiting room. Trucks, ships, or planes become the heroes, carrying these goods to various places.
Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are like the traffic controllers of a warehouse, ensuring everything runs smoothly. These systems help organize and track inventory, making it easier to find and manage products. With WMS, tasks like order picking and packing become more efficient, reducing errors and saving time.
Warehouse Management Systems provide real-time insights into inventory levels and movement. This helps businesses make informed decisions about restocking, preventing shortages or overstock situations. In a nutshell, WMS is the behind-the-scenes hero that keeps warehouses organized, efficient, and ready to meet customer demands.
Order Fulfillment And Distribution Networks

Order fulfillment and distribution networks play a crucial role in getting products from the manufacturer to your doorstep. In simple terms, order fulfillment is the process of receiving, processing, and delivering orders to customers. It involves picking products from the inventory, packing them securely, and shipping them out efficiently.
These networks involve a strategically organized system of warehouses, transportation, and delivery channels. The 5 Basic Steps Of Supply Chain Management play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of these distribution networks. The goal is to optimize the movement of goods, reducing costs, and ensuring timely deliveries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five basic supply chain management processes?
Supply chain management involves five key processes that ensure products reach consumers efficiently. First, there’s planning, where decisions are made about what to produce and in what quantities.
What are the five stages of supply chain management?
Supply chain management involves five key stages that work together seamlessly. First, there’s the planning stage where decisions on what to produce and how much are made.
What is the process of SCM?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the step-by-step journey a product takes from creation to reaching the hands of consumers. It all begins with planning, where companies decide what to produce, how much, and when.
Conclusion
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the backbone of efficient product delivery. It starts with thoughtful planning, determining what to produce and how much. The sourcing phase ensures materials are secured, paving the way for production. Distribution follows, seamlessly delivering the final product to consumers or retailers.
In essence, SCM orchestrates a symphony of interconnected steps. Each phase contributes to the overall harmony of bringing goods from concept to the hands of those who need them. Optimizing these fundamental steps, businesses can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the ever-growing demands of the market.